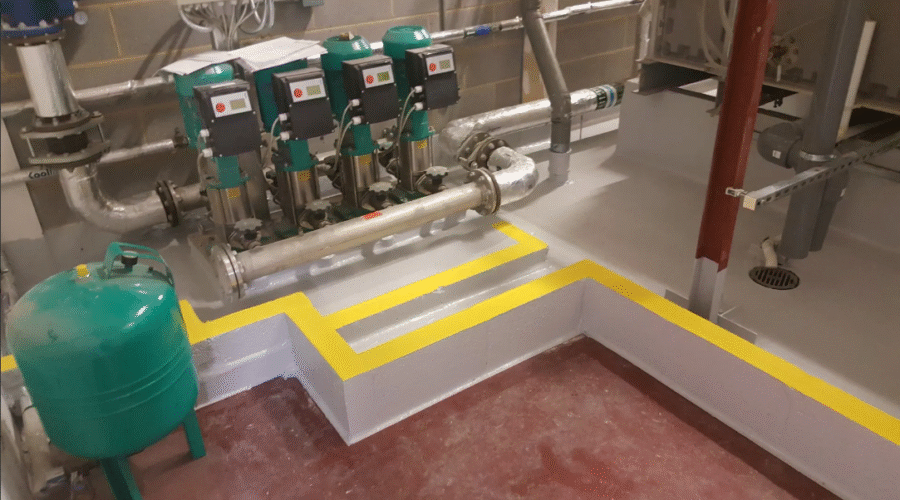
A plant room bund is an essential safety feature in facilities that manage machinery or store liquids such as fuel, oil, or chemicals. Serving as a secondary containment system, a plant room bund is designed to prevent environmental contamination and structural damage caused by leaks or spills. Whether in industrial plants, commercial buildings, hospitals, or data centers, bunds play a vital role in risk management, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection.
Understanding What a Plant Room Bund Is
A plant room bund is a physical barrier, usually built around tanks, generators, or chemical containers within plant rooms. Its primary function is to capture and contain any accidental spills or leaks that may occur from equipment or pipelines. The structure is typically constructed from reinforced concrete, steel, or chemical-resistant plastic, ensuring it can withstand the specific materials it is designed to contain.
This containment system is particularly important in mechanical rooms, boiler plants, and HVAC service areas where the risk of fluid leaks is higher due to continuous machinery operation and fluid circulation.
Why a Plant Room Bund Is Necessary
Installing a plant room bund is not merely a precautionary measure; in many sectors, it is a regulatory requirement. A properly functioning bund protects the surrounding environment from hazardous leaks and supports workplace safety standards. More specifically, it helps:
Also, explore Wellness with by justalittlebite jalbitehealth guides
-
Prevent chemical spills from reaching drainage systems or groundwater
-
Reduce fire hazards caused by flammable liquids
-
Limit the spread of contamination within a building
-
Minimize cleanup costs and operational downtime
Failure to include effective bunding systems can result in non-compliance with environmental laws, heavy fines, and reputational damage.
Key Design Considerations
When planning a plant room bund, several factors must be taken into account to ensure it performs effectively:
-
Volume Capacity
A bund must hold at least 110% of the volume of the largest container it surrounds or 25% of the total volume of all containers—whichever is greater. -
Material Compatibility
Bunds should be built with materials that resist chemical corrosion, especially when storing acids, fuels, or oils. -
Impermeability
To be effective, a bund must be completely watertight. This requires proper sealing and coating to prevent seepage over time. -
Maintenance Access
Design must allow for regular inspection and cleaning without compromising safety or performance. -
Drainage System
A well-designed sump pit and drainage outlet with valves ensure safe liquid removal while preventing backflow.
Industries That Rely on Plant Room Bunds
Plant room bunds are found in numerous environments where hazardous material containment is essential:
-
Healthcare facilities use bunds to manage generator fuel or chemical disinfection fluids.
-
Manufacturing plants rely on bunds to contain oils and solvents used in production.
-
Commercial buildings install bunds in HVAC and fire protection systems to manage fluid leaks.
-
Energy facilities use bunds around transformers and backup power systems.
In all these sectors, bunds contribute to occupational safety, facility protection, and sustainability goals.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance
To maximize the efficiency of a plant room bund, follow these practices:
-
Routine inspections for cracks, corrosion, and fluid accumulation
-
Record keeping for maintenance and cleaning activities
-
Training staff in bund management and spill response procedures
-
Updating systems as part of facility upgrades or compliance audits
These steps ensure the bund remains a reliable component of your safety infrastructure.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a plant room bund?
A plant room bund is designed to contain spills and leaks from equipment in a plant room, preventing environmental contamination and enhancing workplace safety.
2. How often should a plant room bund be inspected?
It is recommended to inspect bunds at least once every six months or after any major incident involving equipment leaks.
3. Are there regulations requiring bund installation?
Yes, environmental and occupational safety regulations often mandate bunding where hazardous liquids are stored or used.
4. What materials are best for constructing a bund?
Reinforced concrete is commonly used, though steel and chemical-resistant plastics are also suitable depending on the stored substance.
5. Can a bund be retrofitted into an existing plant room?
Yes, bunds can be retrofitted, but this process should be handled by qualified professionals to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
Conclusion
A plant room bund is an indispensable feature in any facility that stores or uses hazardous liquids. It supports environmental sustainability, prevents costly damage, and ensures regulatory compliance. By understanding its importance, implementing proper design standards, and maintaining it diligently, facility managers and engineers can safeguard both their operations and the environment. Whether for new construction or existing infrastructure, investing in a high-quality plant room bund is a proactive step toward responsible facility management.